
Blockchain
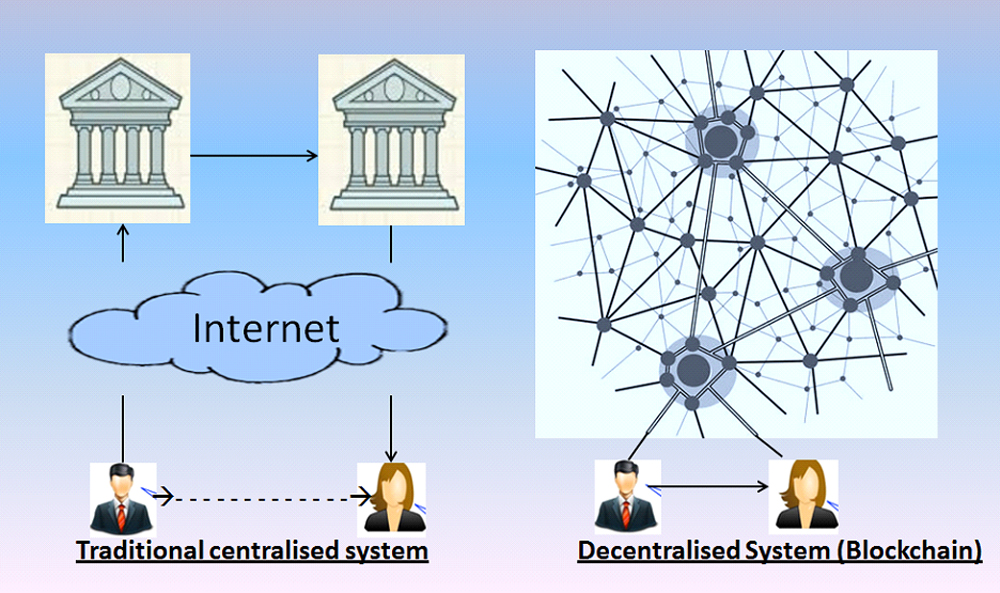
Blockchain is a data storage and transmission technology. By extension, this term describes a decentralised digital database. Often likened to a ledger, this database contains records of electronic transactions (this is the "chain" in Blockchain).
This technology enables users who do not know each other and who are connected via a network to:
- carry out almost real-time transactions using the same application
- bypass intermediaries such as banks, notaries, property registers, etc.
- ensure the reliability and the security of their transactions
Why are they a focus of attention?
Blockchain is a major innovation and is the technology behind the Bitcoin, but its use is not limited to the banking sector. It ensures a transparency of exchanges that could change the way in which our centralised regulatory systems function, reduce costs and transform many areas such as insurance, real estate, trade, elections, etc.
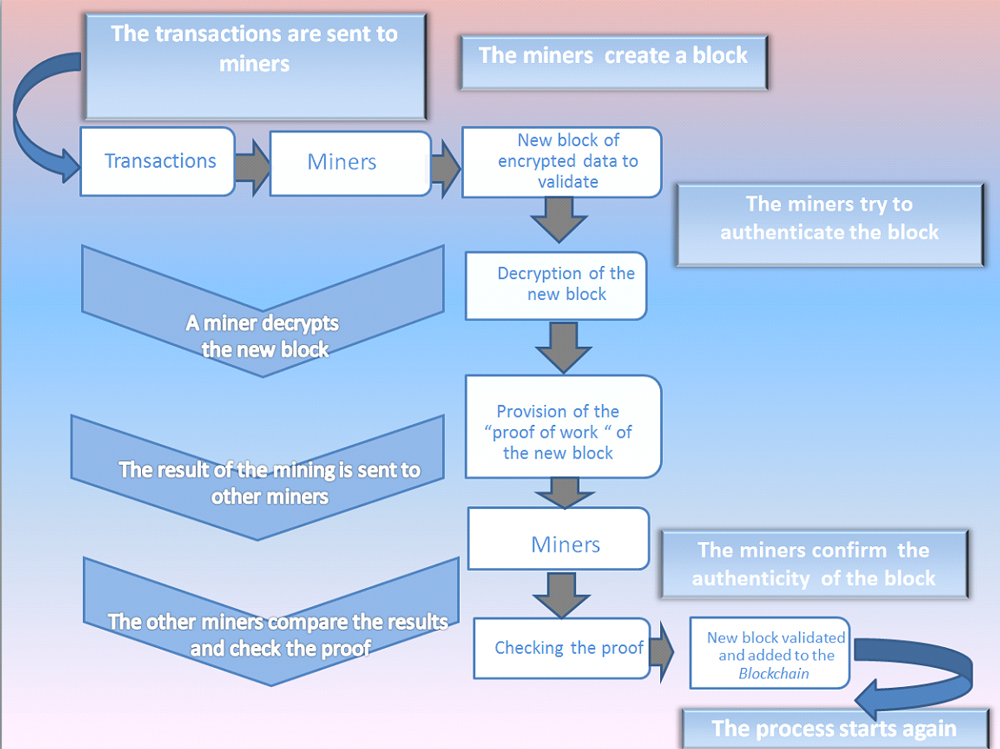
How does this work?
- The parties (buyers, sellers) are identified via an encryption process;
- The transaction is sent to a network (or "storage node)" of computers located throughout the world;
- Each "node" hosts a copy of the database in which the transaction history is stored. All parties can access it simultaneously;
- The security system uses a node consensus mechanism each time information is added. Data are decrypted and authenticated by "data centres" or "miners". The transaction validated in this way is added in the form of a block of encrypted data (this is the "block" in blockchain) ;
- The decentralisation of security management prevents transactions from being faked. Each new block added to the blockchain is linked to the previous one and a copy is sent to all the "nodes" in the network. Each entry is chronological, permanent and unforgeable.
Description of the simplified process
Download the PDF version of this document

publication
Words in the news Blockchain
- Published on 12/12/2016
- 2 pages
- EN
- PDF (298.67 KB)
Updated on: 12/12/2016 14:34